Bankart Repair
What is Bankart Repair?
A Bankart repair, also referred to as shoulder stabilisation surgery or anterior labral repair, is a surgical procedure performed to repair a Bankart lesion, a specific type of injury to the shoulder.
The Bankart lesion is an injury of the shoulder's anterior-inferior glenoid labrum due to shoulder dislocation. When a shoulder dislocates, the labrum (a ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint) can be torn, and the stabilising ligaments attached to it can also be damaged.
A Bankart repair involves reattaching this torn piece of labrum back to the shoulder socket, which often restores stability and function to the joint.
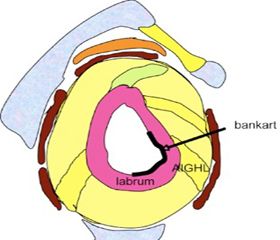
Who is Suitable for Bankart Repair?
Bankart repair is suitable for individuals who have experienced traumatic shoulder dislocations leading to a Bankart lesion. People with persistent shoulder instability, pain, or inability to perform regular activities or participate in sports due to shoulder problems may also be candidates for the procedure. It's often indicated for younger, physically active individuals or athletes who play contact sports. Each case depends on the individual's overall health, injury specifics, and treatment goals.
Benefits of Bankart Repair
The main benefit of a Bankart repair is the restoration of shoulder stability, which can significantly reduce the risk of future dislocations. It can also improve the range of motion, alleviate pain, and enhance the overall function of the shoulder. Following rehabilitation, patients often return to their normal activities and sports.
Types of Bankart Repair Surgery
There are generally two types of Bankart repair surgeries: open and arthroscopic.
- Open Bankart Repair: This is the traditional method where a larger incision is made in the shoulder to access the joint and perform the repair.
- Arthroscopic Bankart Repair: This minimally invasive procedure involves several small incisions. The surgeon uses an arthroscope (a small camera) to guide small surgical instruments for the repair.
The choice between the two typically depends on the surgeon's experience and the specifics of the injury. Both types of surgery aim to reattach and secure the torn labrum back to the shoulder socket. In the current medical practice, arthroscopic Bankart repair is commonly preferred due to its minimally invasive nature.
Alternative Options to Bankart Repair
Before the surgical intervention, non-surgical treatment options such as physical therapy and medication might be tried to manage symptoms and improve shoulder function. This typically includes strength training exercises and stretching to improve shoulder stability. However, surgical intervention may be necessary for those with repeated dislocations and persistent instability.
In addition to the Bankart repair, there are other surgical options to treat shoulder instability:
- Latarjet Procedure: This surgery involves transferring a small piece of bone with an attached tendon to the shoulder joint. It is often used in cases where there is significant bone loss from the shoulder socket or in cases where a previous Bankart repair has failed.
- Capsular Shift: In this procedure, the surgeon tightens the shoulder joint capsule to increase stability.
- Remplissage: This procedure addresses a Hill-Sachs lesion (a dent in the humeral head that occurs with shoulder dislocations). It involves filling the defect with nearby tissue to prevent further instability.
What to Do Before a Bankart Repair?
Before a Bankart repair, a patient will undergo a physical examination and various imaging studies (like an MRI or CT scan) to assess the extent of the injury. The patient should discuss their complete medical history with the surgeon, including allergies and any medications currently being taken.
Patients are generally advised to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, several days before the surgery to reduce the risk of bleeding. They will also be asked to fast (no food or drink) for a few hours before the surgery.
Smokers will be advised to quit before surgery, as smoking can delay healing. Lastly, arranging for a friend or family member to drive the patient home after surgery would also be necessary, as they cannot drive after the procedure.
Arthroscopic Bankart Repair Surgery
During an arthroscopic Bankart procedure, small incisions are made over your shoulder joint.
- An arthroscope, a slender tubular device with a light and a small video camera at the end, is inserted into your shoulder joint through one of the incisions.
- The video camera transmits the image of the inside of your shoulder joint onto a television monitor for your surgeon to view.
- Small surgical instruments are placed through the other incisions to define and mobilise the torn labrum.
- Suture anchors are then inserted to reattach the labrum to the glenoid and tension the attached ligaments.
- The incisions are then closed and covered with a bandage.
Arthroscopy causes minimal disruption to the other shoulder structures and does not require division of the anterior shoulder tendon (subscapularis) as with the open technique.
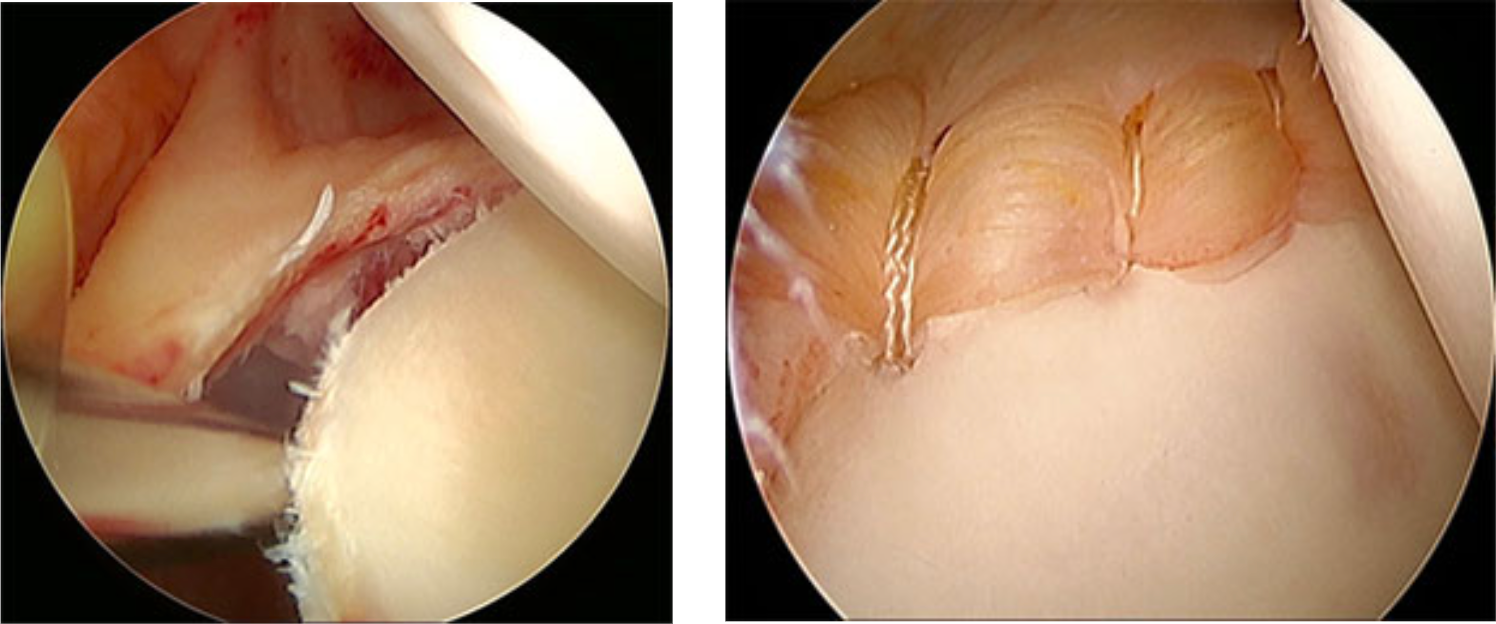
What to Expect After a Bankart Repair?
The patient is taken to the recovery room, where they are closely monitored as the anaesthesia wears off. The shoulder will be immobilised with a sling to protect the repair and promote healing.
Bankart Repair Recovery Plan
Following a Bankart repair, patients will need a recovery plan, which typically includes the following:
- Rest and Immobilisation: The shoulder is usually immobilised with a sling for a few weeks following surgery to protect the repair and allow the tissues to heal.
- Pain Management: Patients are given pain medications to help manage post-operative discomfort.
- Physical Therapy: This is a crucial part of recovery and begins shortly after surgery. Initially, gentle range-of-motion exercises are performed under the guidance of a physical therapist. As healing progresses, more challenging exercises are introduced to improve strength and flexibility.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular surgeon and physiotherapy visits are necessary to monitor the healing process and ensure recovery is progressing as expected.
Bankart Repair Prognosis
The prognosis following a Bankart repair is generally good, with many patients experiencing a significant reduction in shoulder dislocations and improvements in shoulder function. However, the success of the surgery largely depends on the extent of the initial injury, the quality of the surgical repair, and the patient's adherence to the rehabilitation program. Most patients can return to their previous activities, including sports, within 4 to 6 months.
Bankart Repair Risks
As with any surgery, there are risks associated with Bankart repair. These include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Damage to surrounding nerves or blood vessels
- Anaesthesia complications
- Failure of the repair leading to recurrent dislocations
- Stiffness or loss of motion in the shoulder
Discussing these potential risks with your surgeon before the procedure is important.
What if Bankart Repair is Delayed?
Delaying a Bankart repair might increase the risk of further shoulder dislocations, which could lead to additional damage to the shoulder joint. This might include increased tearing of the labrum, damage to the socket's (glenoid) bone, or forming a large Hill-Sachs lesion. Each subsequent dislocation can make the shoulder more unstable, ultimately making the surgical repair more complex and potentially decreasing the chance of a successful outcome. It's recommended to consult with an orthopaedic surgeon to understand the best course of action based on the individual's specific circumstances.